|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Navigation: 5. Detailed description of the Actions > 5.4. Join Tables > 5.4.7 Interval Join (High-Speed
|
Icon: 
Function: IntervalJoin
Property window:
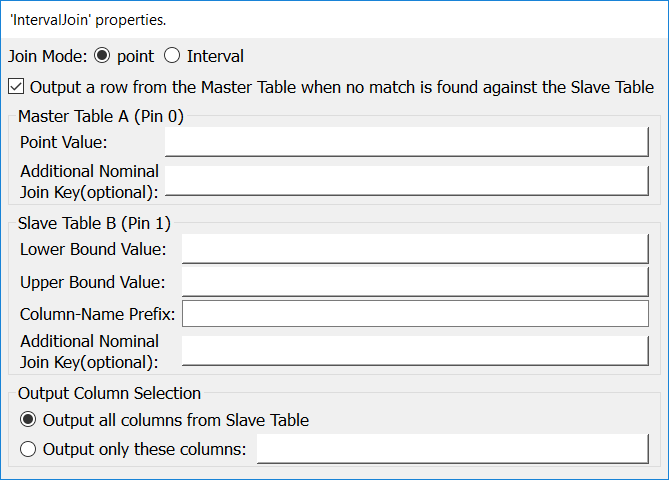
Short description:
Joins two tables based on an interval.
Long Description:
Change the Data Type of some columns, for example time range, income range, age range, etc.
There are two operating modes: point mode, and interval mode.
In the point mode, the master table contains a single continuous value that will seek an interval match in the slave table.
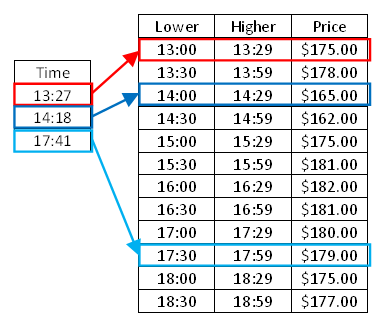
For example, let’s imagine we need to get a quote price depending on the time of the day, we would look in the “slave” table which interval corresponds to the transaction time. The interval is considered as [LOWER, UPPER[, which means you always need to consider that your upper bound is excluded. The additional nominal key typically identifies a customer or a transaction ID that is present in both tables
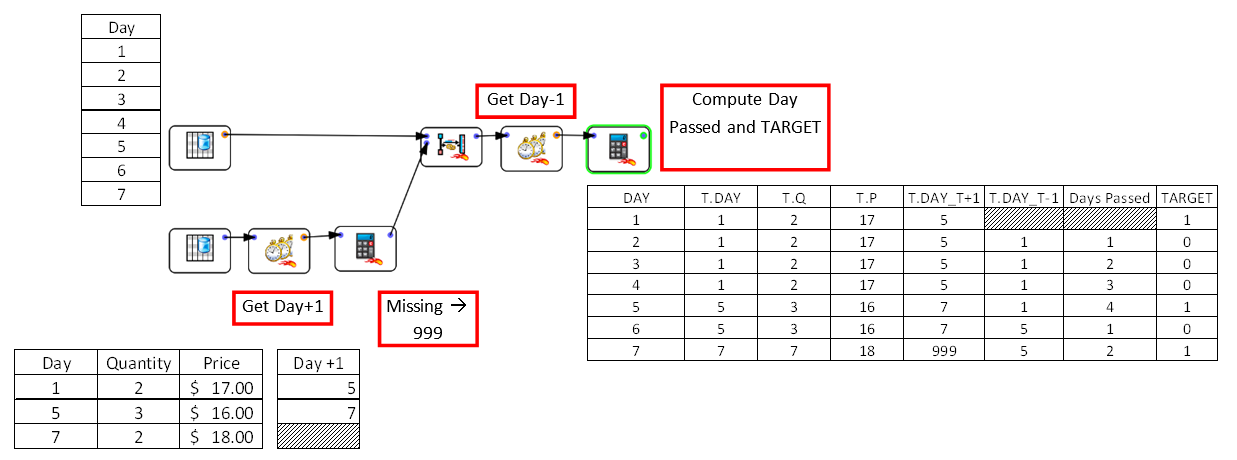
A common setting to use the interval join (and probably one of the conceptually most complex transformation necessary in time-based predictive modeling – hint: certification question) is to prepare data for predictive modelling in which a day is a predictive reference, and we need to keep the information of the last purchase in each prediction window, with only a variation of “time passed”. For this, we create an artificial table in which there is a possible transaction every day and make some relatively complex computations to account for the “upper bound excluded” constraint.
In this example, the prefix “T.” applies to the slave table.