ODBC is a generic technique to access the content of almost any relational databases.
ODBC is the oldest technique available to access data contained into relational databases.
All the databases have an ODBC driver.
The ![]() readODBC action (see section 5.2.3), the
readODBC action (see section 5.2.3), the ![]() upsertODBC action (see section 5.26.4), the
upsertODBC action (see section 5.26.4), the ![]() CreateTable action (see section 5.26.5) and the
CreateTable action (see section 5.26.5) and the ![]() TeradataWriter action (see section 5.26.19) all require an ODBC connection to work.
TeradataWriter action (see section 5.26.19) all require an ODBC connection to work.
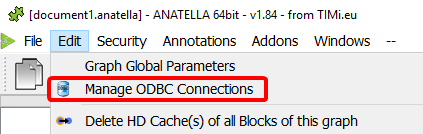
To setup a new ODBC connection for use inside Anatella, you go to the “Manage OBC Connections” window. You can access this window in two different ways:
•Inside the drop-down menu “Edit”, click the “Manage OBC Connections” option:
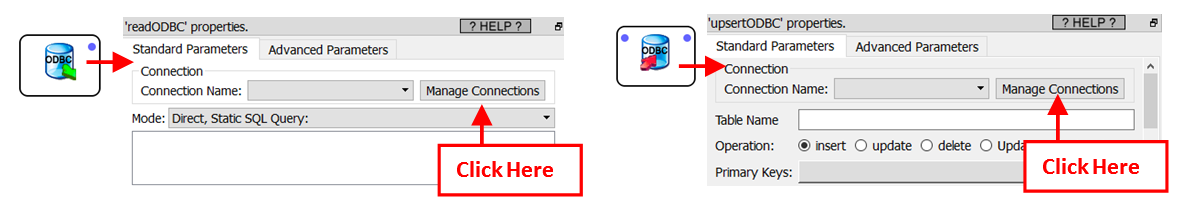
•Click the “Manage Connections” button inside the properties of the ![]() readODBC action or the
readODBC action or the ![]() upsertODBC action:
upsertODBC action:
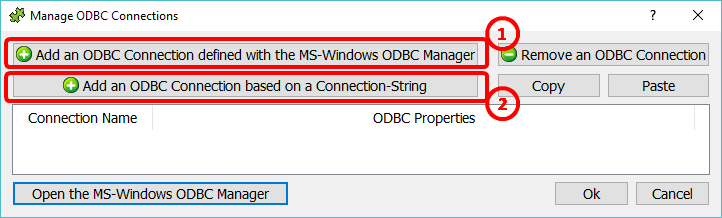
Inside the “Manage OBC Connections” window, you can add&define two different types of ODBC connections:
•Type 1: An ODBC connection that was defined with the MS-Windows ODBC Manager: Click here: ![]()
•Type 2: An ODBC connection based on a connection string: Click here: ![]()
Each ODBC connection type (“Type 1” or “Type 2”) has its PRO’s and CON’s:
Topic |
Type 1 |
Type 2 |
Comments |
Compatibility |
Always supported |
Only supported by a limited number of ODBC drivers |
“Type 2” is supported by Oracle, MS-SQL Server, Teradata, DB2.
“Type 2” is unsupported by PostgreSQL, MySQL. |
Administrative rights |
Required |
Not required |
Administrative rights are required to create&edit the “ODBC DSN” inside the MS-Windows ODBC manager (not to use it). |
Documentation |
Extensive |
Partial |
Very often, the parameters of the “Type2” ODBC connections are not well documented by the database vendors.
In opposition, an easy “wizard” based interface is usually provided to create “Type1” ODBC connections (inside the MS-ODBC Manager). |
Deployment |
Complex |
Easy |
The “Type2” ODBC connections are easier to deploy because once the connection-string to your database is working, it’s very easy to copy-paste it everywhere you need connectivity.
In opposition, creating a “Type1” ODBC connection requires many clicks and editing operations inside the MS-ODBC Manager. Furthermore, only the people with administrative rights can do these editing operations inside the MS-ODBC Manager. |
Robustness |
Low |
High |
Once a “Type2” ODBC connections is setup, it will continue to work, almost indefinitively.
A “Type1” ODBC connection requires the presence of a matching “ODBC DSN” inside the MS-Windows ODBC manager. If this “ODBC DSN” disappear from the MS-Windows ODBC manager (e.g. your administrator removed it), your database connection is broken. |
In the next 2 sections (5.1.6.1 and 5.1.6.2.), we’ll review the procedure step-by-step to create each ODBC connection type (“Type 1” or “Type 2”). The sections from 5.1.6.3 to 5.1.6.6. give more explanations on the detailed setup of the ODBC drivers of each database.