Icon: 
Function: readExcel
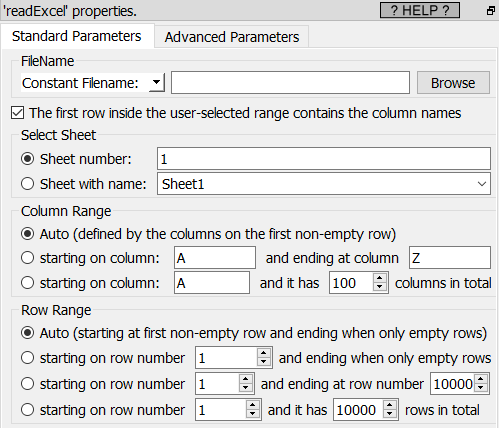
Property window:
Short description:
Reads the newer a Microsoft Excel .xlsx file.
Long Description:
The ![]() readExcel action only reads the newer excel file formats: i.e. the files with the extentions .xlsx and .xlsm. If you need to import into Anatella some data stored into the older excel file format (from the older version of Excel before 2003; i.e. the files with the extensions .xls or .xlt), you should use the
readExcel action only reads the newer excel file formats: i.e. the files with the extentions .xlsx and .xlsm. If you need to import into Anatella some data stored into the older excel file format (from the older version of Excel before 2003; i.e. the files with the extensions .xls or .xlt), you should use the ![]() readExcelOld action (see section 5.2.33. for more details about this action). Don’t worry about selecting the
readExcelOld action (see section 5.2.33. for more details about this action). Don’t worry about selecting the ![]() or the
or the ![]() action: Just drag&drop your Excel file inside the Anatella window and Anatella will take care of the rest.
action: Just drag&drop your Excel file inside the Anatella window and Anatella will take care of the rest.
See section 5.1.1 to have more information on how to specify the filename of the .xlsx file (i.e. You can use use the input pin, a relative path, wildcards, and Javascript to specify your filename(s)).
![]()
You can drag&drop a .xlsx file from a MS-File-Explorer-Window into an Anatella-Graph-Window: This will directly create the corresponding ![]() ReadExcel Action inside the Anatella graph.
ReadExcel Action inside the Anatella graph.
Each different cell inside a .xlsx file can have a different Data-Type (i.e. it can be String, Double, Date, etc.). Furthermore, there is no way to a-priori “guess” the most common type used inside a specific column inside an Excel sheet. For these reasons, all the cells inside an Excel file are imported inside Anatella as simple “Strings”.
A Small note about the way Excel handles dates
Excel uses two different ways to store the dates inside the .xlsx files: Dates can either be stored as Strings or integer numbers. The dates that are saved inside a .xlsx file as integer numbers are imported inside Anatella as numbers.
Excel uses two different ways to store the dates× inside the .xlsx files: Dates can either be stored as Strings or as Numbers. The dates that are stored as Strings are always imported inside Anatella without any difficulties.
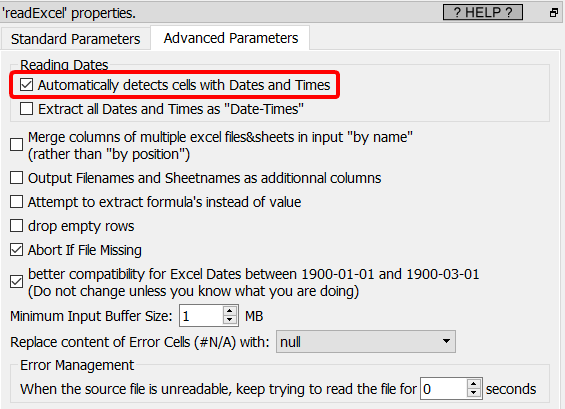
By default, Anatella automatically recognize the “dates×” that are stored as number in MS-Excel .xlsx files and directly import them in a human-readable-format (“yyyyMMdd hh:mm:ss” or “yyyyMMdd” or “hh:mm:ss”). Nothing to worry about.
If you want to avoid this automatic conversion to a “normal, human-readable” dates (and keep the dates as “numbers”), you can uncheck this checkbox:
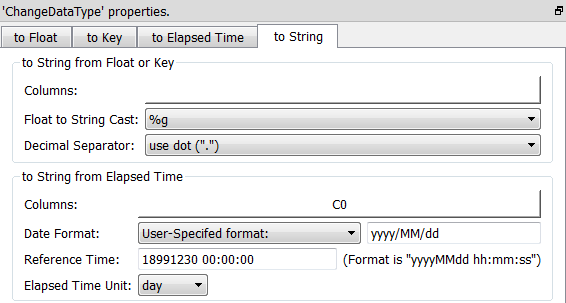
To convert the dates as “numbers” from Excel back to “normal, human-readable” Anatella dates, you can use the “to String from Elapsed Time” option of the ChangeDataType ![]() Action. Use these parameters:
Action. Use these parameters:
•Reference Time: 18991230 00:00:00
•Elapsed Time Unit: day.
Here is a screenshot: